HW 4.20
Nasser Abbasi
Part a
Output
» newtn
newtn - Program to solve a system of nonlinear equations
using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
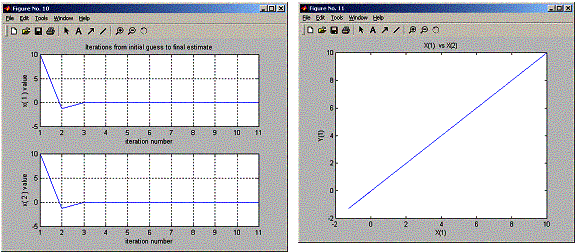
Enter the initial guess (row vector): [10 10]
Enter the parameter a: [10 10^-5 0.1 10 0.1]
Enter number of step to iterate:20
Enter name of your fnewt M file to be called:'nma_HW_4_20_part_a_fnewt'
After 20 iterations the root is
0 0
» newtn
newtn - Program to solve a system of nonlinear equations
using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
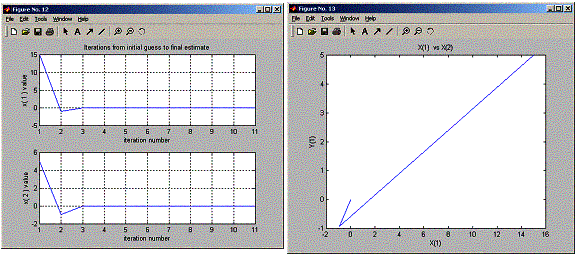
Enter the initial guess (row vector): [15 5]
Enter the parameter a: [10 10^-5 0.1 10 0.1]
Enter number of step to iterate:10
Enter name of your fnewt M file to be called:'nma_HW_4_20_part_a_fnewt'
After 10 iterations the root is
0 0
» newtn
newtn - Program to solve a system of nonlinear equations
using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
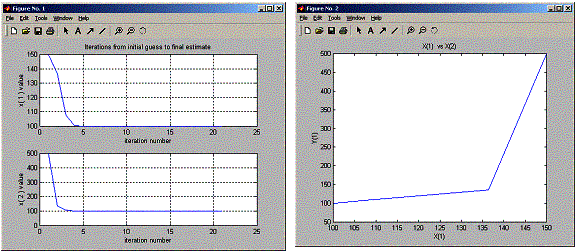
Enter the initial guess (row vector): [150 500]
Enter the parameter a: [10 10^-5 0.1 10 0.1]
Enter number of step to iterate:20
Enter name of your fnewt M file to be called:'nma_HW_4_20_part_a_fnewt'
After 20 iterations the root is
100.0000 99.9900
»
part (b)
» newtn
newtn - Program to solve a system of nonlinear equations
using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
Enter the initial guess (row vector): [10 10]
Enter the parameter a: [2 3]
Enter number of step to iterate:20
Enter name of your fnewt M file to be called:'nma_HW_4_20_part_b_fnewt'
After 20 iterations the root is
1.0e+007 *
1.2599 1.4630
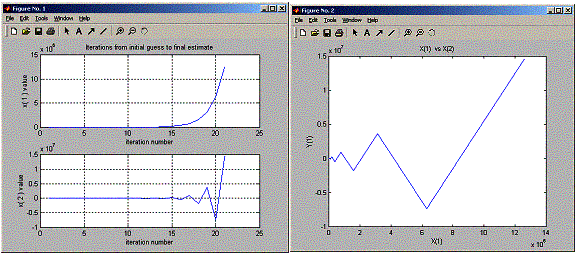
Notice singularity problem when I increased the number
of iterations!
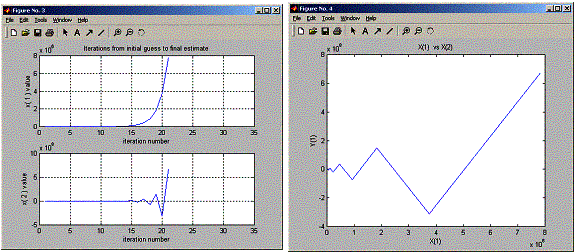
» newtn
newtn - Program to solve a system of nonlinear equations
using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
Enter the initial guess (row vector): [5 300]
Enter the parameter a: [2 3]
Enter number of step to iterate:30
Enter name of your fnewt M file to be called:'nma_HW_4_20_part_b_fnewt'
Warning: Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND = 8.977978e-017.
> In D:\nabbasi\data\nabbasi_web_page\academic\my_courses\phys_240\HW11\newtn.m
at line 25
Warning:
Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND =
2.260851e-017.
>
In D:\nabbasi\data\nabbasi_web_page\academic\my_courses\phys_240\HW11\newtn.m
at line 25
Warning:
Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND =
5.373634e-018.
>
In D:\nabbasi\data\nabbasi_web_page\academic\my_courses\phys_240\HW11\newtn.m
at line 25
Warning:
Matrix is close to singular or badly scaled.
Results may be inaccurate. RCOND =
1.248255e-018.
>
In D:\nabbasi\data\nabbasi_web_page\academic\my_courses\phys_240\HW11\newtn.m
at line 25
Warning:
Matrix is singular to working precision.
>
In D:\nabbasi\data\nabbasi_web_page\academic\my_courses\phys_240\HW11\newtn.m
at line 25
Warning:
Matrix is singular to working precision.
>
In D:\nabbasi\data\nabbasi_web_page\academic\my_courses\phys_240\HW11\newtn.m
at line 25
After
30 iterations the root is
-Inf
-Inf
»
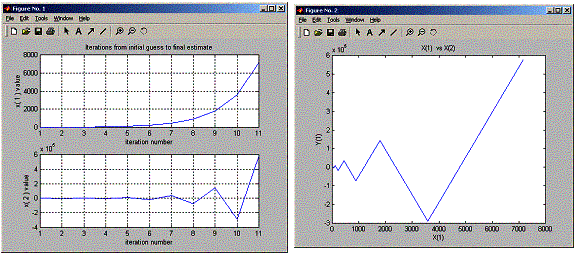
» newtn
newtn - Program to solve a system of nonlinear equations
using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
Enter the initial guess (row vector): [5 300]
Enter the parameter a: [2 3]
Enter number of step to iterate:10
Enter name of your fnewt M file to be called:'nma_HW_4_20_part_b_fnewt'
After 10 iterations the root is
1.0e+005 *
0.0717 5.7968
»
SOURCE CODE
% newtn - Program to solve a
system of nonlinear equations
% using Newton's method. Equations defined by function fnewt.
clear all;
help newtn; % Clear memory and print header
% Modified by Nasser Abbasi to
allow one to enter the
% name of the fnewt M file to
solve for both problems 4.20 part
% a and part b and to do the plots
for two variables model
% instead of the 3 variables as
lorenz model.
%* Set initial guess and
parameters
x0 =
input('Enter the initial guess (row vector): ');
x =
x0; %
Copy initial guess
xp(:,1) = x(:); %
Record initial guess for plotting
a =
input('Enter the parameter a: ');
nStep =
input('Enter number of step to iterate:');
fnewt =
input('Enter name of your fnewt M file to be
called:');
%* Loop over desired number of
steps
for iStep=1:nStep
%* Evaluate function f and its Jacobian matrix D
[f D] =
feval(fnewt,x,a); % fnewt returns value of f and D
%* Find dx by Gaussian elimination
dx
= f/D;
%* Update the estimate for the root
x
= x - dx; % Newton iteration for new x
xp(:,iStep+1)
= x(:); % Save current estimate for plotting
end
%* Print the final estimate for
the root
fprintf('After %g
iterations the root is \n',nStep);
disp(x);
%
%do the plots
%
figure;
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(xp(1,:));
title('Iterations from
initial guess to final estimate');
xlabel('iteration
number');
ylabel('x( 1 ) value');
grid on;
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(xp(2,:));
grid on;
xlabel('iteration
number');
ylabel('x( 2 ) value');
%
% plot x(1) against x(2)
%
figure;
plot(xp(1,:),xp(2,:));
title('X(1) vs X(2)');
xlabel('X(1)');
ylabel('Y(1)');
drawnow;
function [f,D] =
nma_HW_4_20_part_b_fnewt(x,param)
%
Function used by the N-variable Newton's method
%
Inputs
% x State vector
[x y]
% param Parameters [A
B]
%
Outputs
% f Lorenz model
r.h.s. [dx/dt dy/dt dz/dt]
% D Jacobian matrix,
D(i,j) = df(j)/dx(i)
% Modified from original fnewtn to
solve problem 4.18 part b.
% Nasser abbasi
% Evaluate f(i)
f(1) =
param(1)+ (x(1)^2) * x(2) - (param(2)-1) * x(1);
f(2) =
param(2)*x(1) - ((x(1)^2) * x(2) );
% Evaluate D(i,j)
D(1,1) = 2*x(1)*x(2) - param(2)-1; %
df(1)/dx(1)
D(1,2) = param(2)-2*x(1)*x(2); % df(2)/dx(1)
D(2,1) = x(1)^2; %
df(1)/dx(2)
D(2,2) = -x(1)^2; %
df(2)/dx(2)
return;
function [f,D] = nma_HW_4_20_part_a_fnewt(x,param)
%
Function used by the N-variable Newton's method
%
Inputs
% x State vector
[x y]
% param Parameters [a
b c d e]
%
Outputs
% f Lorenz model
r.h.s. [dx/dt dy/dt dz/dt]
% D Jacobian matrix,
D(i,j) = df(j)/dx(i)
% Modified from original fnewtn to
solve problem 4.18 part a.
% Nasser abbasi
% Evaluate f(i)
f(1) = (param(1)- param(2)*x(1) - param(3)*x(2) ) *
x(1);
f(2) = (-param(4) + param(5)*x(1)) * x(2);
% Evaluate D(i,j)
D(1,1) = param(1)- 2*param(2)*x(1)-
param(3)*x(2); % df(1)/dx(1)
D(1,2) = param(5)*x(2); %
df(2)/dx(1)
D(2,1) = -param(3)*x(1); %
df(1)/dx(2)
D(2,2) = -param(4)+param(5)*x(1); %
df(2)/dx(2)
return;