Problem 5.24
Nasser Abbasi
Output
» nma_problem_5_24
nma_problem_5_24 - Program to compute the trajectories
of the Lorenz equations using the adaptive Runge-Kutta method.
then plot the power spectrum for z(t) solves problem 5.25
page 170
original program called lorenz, modified by Nasser Abbasi
Enter the initial position [x y z]: [1 1 20]
Enter the parameter r: 28
Enter number of steps: 1024
Finished 50 steps out of 1024
Finished 100 steps out of 1024
Finished 150 steps out of 1024
Finished 200 steps out of 1024
Finished 250 steps out of 1024
Finished 300 steps out of 1024
Finished 350 steps out of 1024
Finished 400 steps out of 1024
Finished 450 steps out of 1024
Finished 500 steps out of 1024
Finished 550 steps out of 1024
Finished 600 steps out of 1024
Finished 650 steps out of 1024
Finished 700 steps out of 1024
Finished 750 steps out of 1024
Finished 800 steps out of 1024
Finished 850 steps out of 1024
Finished 900 steps out of 1024
Finished 950 steps out of 1024
Finished 1000 steps out of 1024
»


source code
%
nma_problem_5_24 - Program to compute the trajectories
% of the
Lorenz equations using the adaptive
Runge-Kutta method.
% then
plot the power spectrum for z(t) solves problem 5.25
% page
170
%
original program called lorenz, modified by Nasser Abbasi
clear; help nma_problem_5_24;
%* Set
initial state x,y,z and parameters r,sigma,b
state = input('Enter the initial position [x y z]: ');
r = input('Enter the parameter r: ');
sigma = 10.; % Parameter
sigma
b = 8./3.; %
Parameter b
param = [r sigma b]; % Vector of
parameters passed to rka
tau = 0.05; %
timestep
%* Loop
over the desired number of steps
time = 0;
nstep = input('Enter number of steps: ');
for istep=1:nstep
z_timeSeries(istep) = state(3);
% save for power spectrum
%* Record values for plotting
x = state(1);
y = state(2);
z = state(3);
tplot(istep) = time;
tauplot(istep) = tau;
xplot(istep) = x;
yplot(istep) = y;
zplot(istep) = z;
if( rem(istep,50) < 1 )
fprintf('Finished %g steps out of
%g\n',istep,nstep);
end
%* Find
new state using adaptive Runge-Kutta
% [state, time, tau] = rka(state,time,tau,err,'lorzrk',param);
state = rk4(state,time,tau,'lorzrk',param);
time = time + tau;
end
%* Graph
the time series z(t)
figure(1); clf; % Clear
figure 1 window and bring forward
plot(tplot,zplot,'-')
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('z(t)')
title('Lorenz model z(t) time series')
pause(1) % Pause 1
second
%* Graph
the x,y,z phase space trajectory
figure(2); clf; % Clear
figure 2 window and bring forward
% Mark
the location of the three steady states
x_ss(1) = 0; y_ss(1) = 0; z_ss(1) = 0;
x_ss(2) =
sqrt(b*(r-1)); y_ss(2) = x_ss(2);
z_ss(2) = r-1;
x_ss(3) = -sqrt(b*(r-1));
y_ss(3) = x_ss(3); z_ss(3) = r-1;
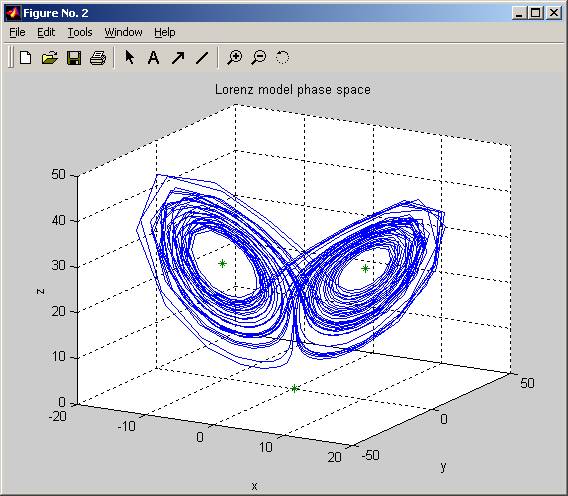
plot3(xplot,yplot,zplot,'-',x_ss,y_ss,z_ss,'*')
view([30 20]); % Rotate to
get a better view
grid; %
Add a grid to aid perspective
xlabel('x'); ylabel('y');
zlabel('z');
title('Lorenz model phase space');
%
% power
spectrum
%
f(1:nstep) =
(0:(nstep-1))/(tau*nstep); % Frequency
z_fft = fft(z_timeSeries); % Fourier
transform of z displacement
z_spect =
abs(z_fft).^2; % Power spectrum of z displacement
%* Apply
the Hanning window to the time series and calculate
% the resulting power spectrum
window =
0.5*(1-cos(2*pi*((1:nstep)-1)/nstep)); %
Hanning window
z_w = z_timeSeries' .*
window'; % Windowed time series
zw_fft = fft(z_w); %
Fourier transf. (windowed data)
z_spectw = abs(zw_fft).^2; % Power
spectrum (windowed data)
%* Graph
the power spectra for original and windowed data
figure;
semilogy(f(1:(nstep/2)),z_spect(1:(nstep/2)),'b-',...
f(1:(nstep/2)),z_spectw(1:(nstep/2)),'r-');
title('Power spectrum for z(t) displacment (dashed is
windowed data)');
xlabel('Frequency'); ylabel('Power');
legend('non-window data','window
data');