problem:
Consider SLP \(-y^{\prime \prime }=\lambda y\), \(0<x<1\) with B.V. \(y\left ( 0\right ) +y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =0,y\left ( 1\right ) =0\)
is \(\lambda =0\) an eigenvalue? are there negative eigenvalues? show that there are infinitely many positive eigenvalues by finding an equation whose roots are those eigenvalues and show graphically that there are infinity many root
answer:
The SLP has the form \(-\left ( p\left ( x\right ) y^{\prime }\right ) ^{\prime }+\left ( q\left ( x\right ) -\lambda \right ) y=0\) or \(-\left ( p\left ( x\right ) y^{\prime }\right ) ^{\prime }+q\left ( x\right ) y=\lambda y~\)for \(a\,<x<b\), where \(p\left ( x\right ) \) not zero function and does not change sign over the interval, hence we can assume it to be positive. If we compare this form to the given problem we see that \(p\left ( x\right ) =1\) and \(q\left ( x\right ) =0\)
Assume \(\lambda =0\), hence the ODE become \(-y^{\prime \prime }=0\) which has the solution \(y=Ax+B\) for some constants \(A,B\). Now lets see is this solution can satisfy the B,V, given.
\(y\left ( 1\right ) =0\rightarrow A+B=0\), and \(y\left ( 0\right ) +y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =0\rightarrow A=0\), hence since \(A=0\), then \(B=0\) hence the only solution is \(y\left ( x\right ) =0\). Hence for non-trivial solution \(\lambda \neq 0\)
Now let us assume \(\lambda <0\). Assume \(y=Ae^{mx}\), hence the characteristic equation is \(-m^{2}=\lambda \) or \(m^{2}=-\lambda \), but since \(\lambda <0\), then \(m\) is a real quantity. Let \(-\lambda =\beta ^{2}\) where \(\beta \) is some non zero real constant, hence we have \(m=\pm \beta \) and so the solution is
Let see is this solution will satisfy the B.V. \(y\left ( 1\right ) =0\rightarrow 0=c_{1}e^{\beta }+c_{2}e^{-\beta }\), and \(y\left ( 0\right ) +y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =0\rightarrow c_{2}+c_{1}=0\), hence \(c_{1}=-c_{2}\), and we have \(-c_{2}e^{\beta }+c_{2}e^{-\beta }=0\), hence \(c_{2}\left ( e^{-\beta }-e^{\beta }\right ) =0\), or but \(e^{-\beta }-e^{\beta }\neq 0\) (it is zero only if \(\beta =0\) but we have that \(\beta >0\)) then this means that \(c_{2}=0\). But this means that \(c_{1}=0\), which then means that the solution is again \(y\left ( x\right ) =0\). Therefore, for non-trivial solution, \(\lambda \) can not be negative.
. (We do not have to check for this, since we know that \(\lambda \) does not change sign) but for an exercise, let us verify it any way. As above, we obtain \(m^{2}=-\lambda \) but since \(\lambda >0\) then solution will now contain complex exponential since \(m=\pm i\sqrt {\lambda },\) then solution is (by writing\(\sqrt {\lambda }=\beta )\)
Verify B,V, The first one leads to
and the second one leads to, since \(y^{\prime }\left ( x\right ) =-c_{1}\beta \sin \beta x+c_{2}\beta \cos \beta x\), we obtain
or \(c_{1}=-\beta c_{2}\), now substitute this in the first initial condition (1) we obtain
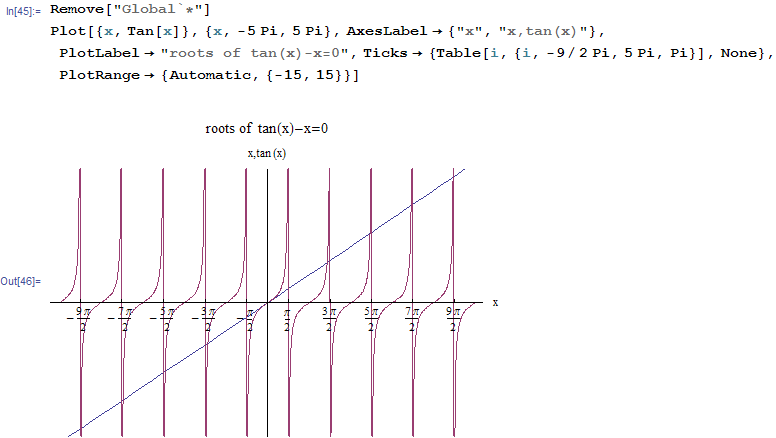
But if \(c_{2}=0\) this will lead to \(c_{1}=0\) also and to a trivial solution. Hence we need to consider \(\sin \beta -\beta \cos \beta =0\) or roots of
The roots are the intersection of \(\tan \left ( x\right ) \) with the line \(x\), graphically we see the roots occur close to multiplies of \(\frac {\pi }{2}\)

Or we can just plot the function \(\sin \beta -\beta \cos \beta \)
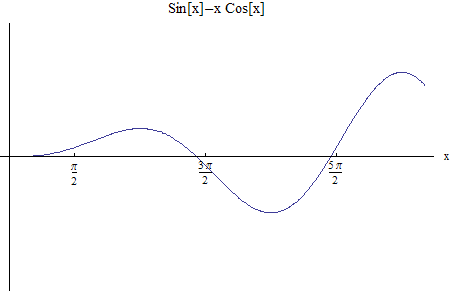
To find the roots, use a numerical root finder (Newton’s method), here are the first 10 positive roots (we do not pick the zero root, since \(\lambda \neq 0\))

Hence the square of the above is the list of the eigenvalues. Here are first few
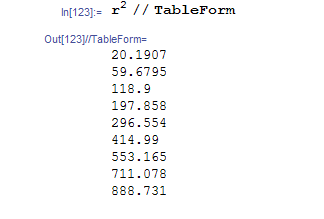
Hence the eigenfunctions are
and
for \(n=1,2,3,\cdots \) where \(\sqrt {\lambda _{n}}\) is the root of \(\tan \sqrt {\lambda _{n}}-\sqrt {\lambda _{n}}=0\), and the first few \(\lambda _{n}\) are shown above.
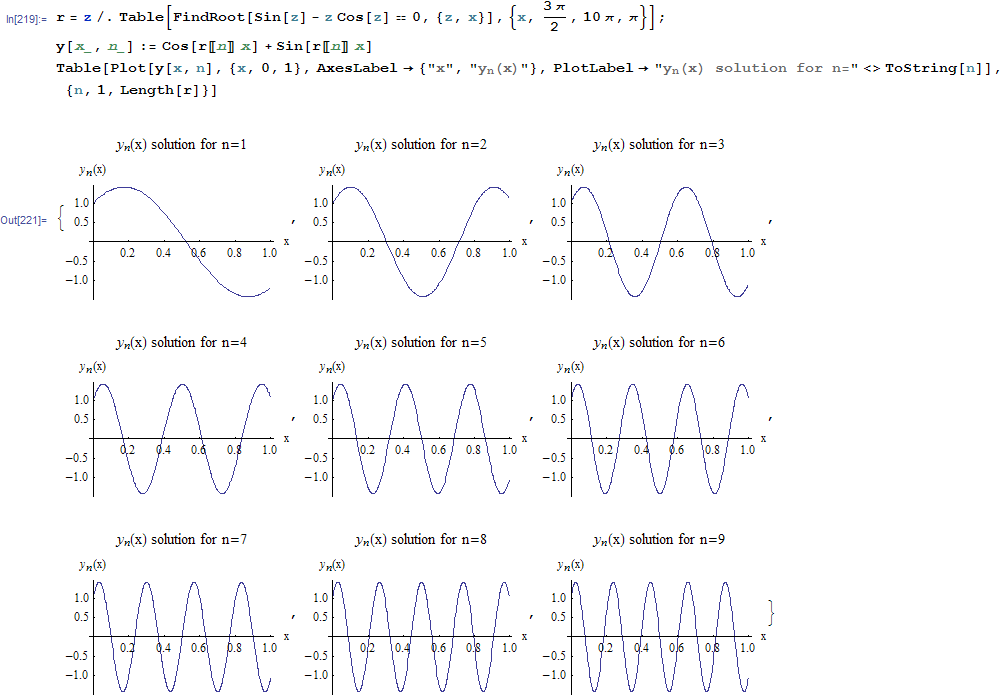
Here is a plot of few solutions for \(n=1\cdots 9\)
problem:
Find eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for the problem \(-y^{\prime \prime }-2by^{\prime }=\lambda y\), \(0<x<1\) \(,b>0\), and \(y(0)=y\left ( 1\right ) =0\)
answer:
The SLP has the form \(-\left ( p\left ( x\right ) y^{\prime }\right ) ^{\prime }+q\left ( x\right ) y=\lambda y\) for \(a\,<x<b\), where \(p\left ( x\right ) \) not zero function and does not change sign over the interval, hence we can assume it to be positive. If we compare this form to the given problem we see that \(p\left ( x\right ) =1\) and \(q\left ( x\right ) =-2b\) and since \(b>0\) then \(q\left ( x\right ) \) is always negative over this range
Assume \(\lambda =0\), hence the ODE become \(-y^{\prime \prime }-2by^{\prime }=0\) which has the characteristic equation \(-m^{2}-2bm=0\) or \(-m-2b=0\), hence \(m=2b\), then the solution is \(y=c_{1}xe^{2bx}+c_{2}e^{2bx}\). Now from \(y\left ( 0\right ) =0\rightarrow c_{2}=0\), and so \(y=c_{1}xe^{2bc}\), Now from \(y\left ( 1\right ) =0\rightarrow 0=c_{1}e^{2b}\), but \(e^{2b}\neq 0\) hence \(c_{1}=0\), hence we obtain trivial solution \(y=0\), hence for non-trivial solution \(\lambda \neq 0\) .
Now \(-y^{\prime \prime }-2by^{\prime }=\lambda y\), and the characteristic equation is \(m^{2}+2bm+\lambda =0\), hence \(m=\frac {-2\left ( b\right ) \pm \sqrt {4b^{2}-4\lambda }}{2}\), hence \(m=-b\pm \sqrt {b^{2}-\lambda }\). There are 3 cases: \(b^{2}-\lambda <0\) and \(b^{2}-\lambda =0\) and \(b^{2}-\lambda >0.\)
When \(b^{2}-\lambda >0\), we have \(m\) will be real. Hence the solution will be of the form \(y=c_{1}e^{mx}+c_{2}e^{-mx}\), where \(m\) is real. Now let see if we can satisfy the boundary conditions. From \(y\left ( 0\right ) =0\rightarrow c_{1}+c_{2}=0\), and from \(y\left ( 1\right ) =0\rightarrow 0=c_{1}e^{m}+c_{2}e^{-m}\), hence \(0=c_{1}\left ( e^{m}-e^{-m}\right ) \), but this means \(c_{1}=0\) since \(m\) is not zero. This leads to \(c_{2}=0\) which leads to trivial solution \(y=0\). Therefore \(b^{2}-\lambda >0\) is not possible choice.
When \(b^{2}-\lambda =0\), hence \(m=-b\), then the solution is \(y=c_{1}xe^{-bx}+c_{2}e^{-bx}\), and by similar argument as above for the case of \(\lambda =0\), we conclude that it is not possible to have \(b^{2}-\lambda =0\)
Hence \(b^{2}-\lambda <0\) or \(\lambda >b^{2}\)\(.\) In other words, \(\lambda \) is positive and must be greater than \(b^{2}\). Let \(b^{2}-\lambda =-k^{2}\) for \(k\) real and nonzero. Hence
and the solution is
at \(y\left ( 0\right ) =0\rightarrow \)\(0=c_{1}\) and \(y\left ( 1\right ) =0\rightarrow \)\(0=e^{-b}c_{2}\sin k\)
Hence for non-trivial solution,
or \(k=n\pi \) or \(k^{2}\) \(=n^{2}\pi ^{2}\). But \(k^{2}=\lambda -b^{2}\) Hence \(\lambda _{n}-b^{2}=n^{2}\pi ^{2}\). Now since \(\lambda >b^{2}\) we can eliminate that \(n=0\) case. Then we have
Hence \(\lambda _{1}=b^{2}+\pi ^{2},\lambda _{2}=b^{2}+4\pi ^{2}\ ,\cdots \)
So the eigenfunctions are
where \(k_{n}=\sqrt {\lambda _{n}-b^{2}}\)
So the \(y_{n}\left ( x\right ) \) solution is
problem:
Find eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for the problem with periodic boundary conditions \(-y^{\prime \prime }=\lambda y\), \(0<x<L\) and \(y(0)=y\left ( L\right ) ,y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =y^{\prime }\left ( L\right ) \)
answer:
The SLP has the form \(-\left ( p\left ( x\right ) y^{\prime }\right ) ^{\prime }+q\left ( x\right ) y=\lambda y~\)for \(a\,<x<b\), where \(p\left ( x\right ) \) not zero function and does not change sign over the interval, hence we can assume it to be positive. If we compare this form to the given problem we see that \(p\left ( x\right ) =1\) and \(q\left ( x\right ) =0\)
Assume \(\lambda =0\), hence we have \(y^{\prime \prime }=0\) or \(y\left ( x\right ) =Ax+B\). Now to satisfy \(y(0)=y\left ( L\right ) \,\)we must have \(B=AL+B\) which implies \(A=0\), hence \(y\left ( x\right ) =B\). Now this solution does satisfy \(y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =y^{\prime }\left ( L\right ) \) since \(y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =0\) and \(y^{\prime }\left ( L\right ) =0\ \)hence \(\lambda =0\) is an eigenvalue.
Now Assume \(\lambda <0\). Hence \(y^{\prime \prime }+\lambda y=0\) and characteristic equation is \(m^{2}+\lambda =0\) or \(m^{2}=-\lambda \), since \(\lambda <0\), then \(-\lambda \) is positive, hence this leads to solution of \(y=c_{1}e^{mx}+c_{2}e^{-mx}\) where \(m\) is real. Now to satisfy \(y(0)=y\left ( L\right ) \,\)we must have
and to satisfy \(y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =y^{\prime }\left ( L\right ) \) we must have, since \(y^{\prime }\left ( x\right ) =\) \(c_{1}me^{mx}-c_{2}me^{-mx}\) that
Since \(\lambda \neq 0\) in this case, then \(m\neq 0\) so we can divide by \(m\) and obtain
add (1)+(2) we have
\(2c_{1}=2c_{1}e^{mL}\) or \(e^{mL}=1\) hence \(mL=0\) or \(m=0\) which contradicts our assumption that \(\lambda \neq 0\). So \(\lambda <0\) is not possible.
, Hence \(y^{\prime \prime }+\lambda y=0\) and characteristic equation is \(m^{2}+\lambda =0\) or \(m^{2}=-\lambda \), since \(\lambda >0\), then \(m\) is complex„ hence \(m=\pm i\sqrt {\lambda }\) and this leads to solution of (by letting \(\beta =\sqrt {\lambda }\))
Now to satisfy \(y(0)=y\left ( L\right ) \,\)we must have
and to satisfy \(y^{\prime }\left ( 0\right ) =y^{\prime }\left ( L\right ) \) we must have, since
that
Substitute (3) into (4) we have
Since \(\sqrt {\lambda }\neq 0\) the above becomes
Now \(c_{2}\neq 0\) else this makes \(c_{1}=0\) also and we obtain trivial solution. Hence we must have
Hence
or
Hence
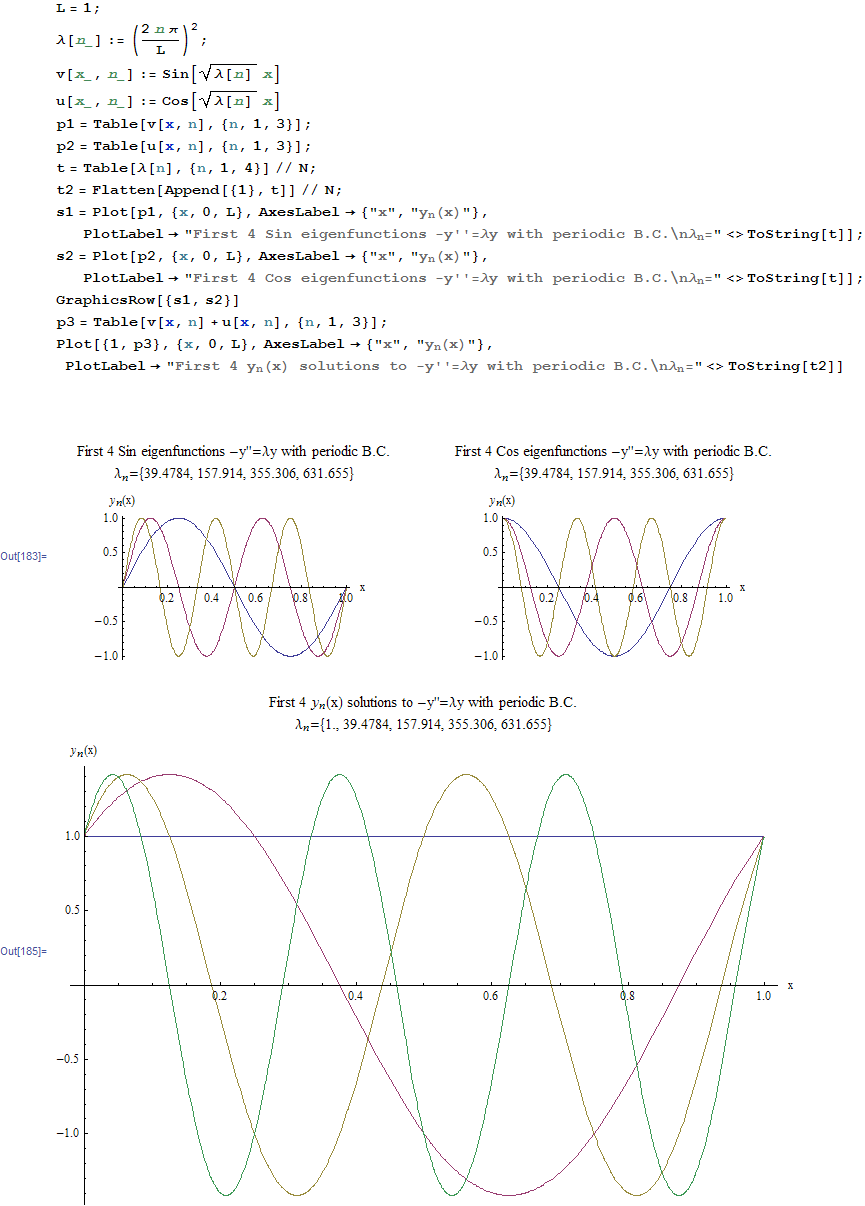
Hence the eigenfunctions are \(\,v_{n}\left ( x\right ) =\sin \beta _{n}x\) and \(u_{n}=\cos \beta _{n}x\)
For \(\lambda _{0}=0\), \(v_{1}\left ( x\right ) =0\) and \(u_{n}=1\rightarrow \)\(y_{0}\left ( x\right ) =1\)
For \(\lambda _{1}=1,2,3,\cdots \) \(\rightarrow v_{1}\left ( x\right ) =\sin \frac {2n\pi }{L}x\) and \(u_{n}=\cos \frac {2n\pi }{L}x\rightarrow \)\(y_{n}\left ( x\right ) =c_{1}\sin \frac {2n\pi }{L}x+c_{2}\cos \frac {2n\pi }{L}x\)
this is a plot of few eigenfunctions \(v_{n},u_{n}\) and the complete solution \(y_{n}=u_{n}+v_{n}\) for first few eigenvalues